问题
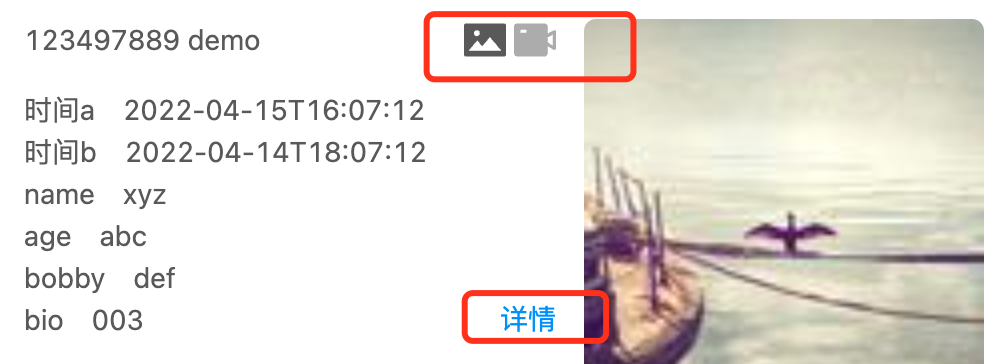
上面的两个icon和详情超级链接,用margin/padding属性无法做到原型稿要求的样式。
解决方案
The position property specifies the type of positioning method used for an element (static, relative, fixed, absolute or sticky).
上面card UI组件的两个svg图标和详情应该使用position: absolute属性,它们最近的祖先div应该使用position: relative属性:
| |
position介绍
The position property specifies the type of positioning method used for an element.
Elements are then positioned using the top, bottom, left, and right properties. However, these properties(top/bottom/left/right) will not work unless the position property is set first.
They(top/bottom/left/right) also work differently depending on the position value.
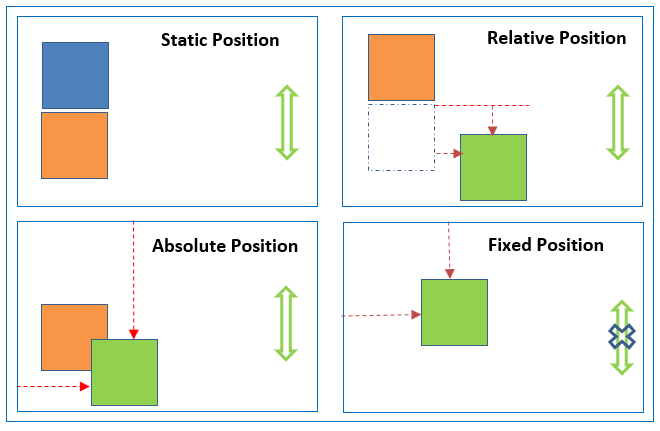
static
HTML elements are positioned static by default.
Static positioned elements are not affected by the top, bottom, left, and right properties.
An element with position: static; is not positioned in any special way; it is always positioned according to the normal flow of the page.
relative
An element with position: relative; is positioned relative to its normal(static) position.
Setting the top, right, bottom, and left properties of a relatively-positioned element will cause it to be adjusted away from its normal position.
Other content will not be adjusted to fit into any gap left by the element.
fixed
An element with position: fixed; is positioned relative to the viewport, which means it always stays in the same place even if the page is scrolled.
The top, right, bottom, and left properties are used to position the element.
A fixed element does not leave a gap in the page where it would normally have been located.
absolute
An element with position: absolute; is positioned relative to the nearest positioned ancestor (instead of positioned relative to the viewport, like fixed).
However; if an absolute positioned element has no positioned ancestors, it uses the document body, and moves along with page scrolling.
Note: Absolute positioned elements are removed from the normal flow, and can overlap elements.
sticky
An element with position: sticky; is positioned based on the user’s scroll position.
A sticky element toggles between relative and fixed, depending on the scroll position.
It is positioned relative until a given offset position is met in the viewport - then it “sticks” in place (like position:fixed).
For example, a sticky element sticks to the top of the page (top: 0), when you reach its scroll position
