之前写了一篇post 适配腾讯云backend 的文章,从代码的角度简单记录了flannel
vpc backend实现过程。
这篇文章是对前面文章的补充,全局鸟瞰描绘了flannel vpc backend网络数据包的流动过程。
总体来看vpc 和 host-gw 模式是很类似的,理解host-gateway模式 对理解vpc 模式很有帮助。
host gw
host gateway 模式:
host-gw adds route table entries on hosts, so that host know how to traffic container network packets.
This works on L2, because it only concerns hosts, switches and containers. switches does not care IP and route, hosts know containers exists, and how to route to them, containers just send and receive data.
If hosts are at different networks, L3 is introduced, and routers are involved. routers have no idea that containers exists, and any containers packet will be dropped, making communication impossible.
Of course, you can add route table entries on routers, but that is out of control flannel.
L2
为什么host-gw模式下,二层网络一定要打通:
stackoverflow 上面已经有很好的回答,我摘抄过来:
host-gw adds route table entires on each host. And the entries are as following:
| |
The most import item is the value of Gateway(10.110.110.21).
The route table will change the destination mac address to the mac_address of node(10.110.110.21) which is connected L2 directly to 10.110.110.22(current node).
If not L2 connected, the packet can not be delivered to nodes(next-hop)
vpc
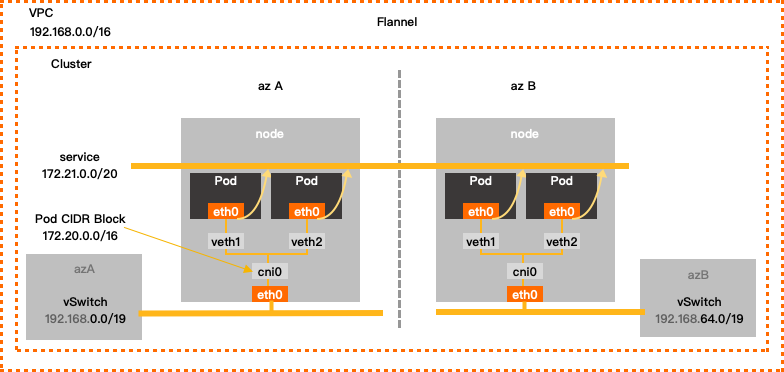
数据包
vpc backend模式下网络数据包的流动过程如下:
- Flanneld 在每个node 节点创建一个 cni0 的网桥bridge设备,node里面的pod之间的通信走cni0网桥;
- Node 和 在本机上的pod 通信通过node的route table 转发到cni0;
- vpc backend适配器调用vpc sdk在vpc网络中维护了一个vpc route table;
- Node 和其它node里面的pod通信,是先通过 vpc route table 找到 pod 子网 所对应node,然后再通过这个node把网络流量转发到pod;
- 跨node 的pod 通信通过这个route table找到pod网段所在的node,然后载通过 node 节点上的route table 转发到对应node 上cni0设备上然后找到对应的pod;
- VPC上的普通vm(即,该vm不是k8s node)和 k8s pod之间的通信与 上面第4,5点 通信是一样的。
L2区别
host-gw mode 因为是在node 节点上 添加的 route 规则,所以所有的节点要二层switch打通,否则 下一跳(next-hop)跳不过去,没人帮忙转发二层数据包(frame)。
vpc backend mode 因为是在云厂商提供的外部router上添加的 route 规则,对vm做到了无感知,所以 vm之间无需打通 二层 switch。